The Explainer Ontology
- Latest version:
- https://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer
- Contributors:
- Anjana Wijekoon
- Chamath Palihawadana
- David Corsar
- Ikechukwu Nkisi-Orji
- Juan A. Recio-Garcia
- Marta Caro Martínez
- Imported Ontologies:
- explanationPattern.owl
- sio.owl
- cpannotationschema.owl
- prov-o#
- eo
- Download serialization:
- Visualization:
- Cite as:
- The Explainer Ontology.
Abstract
The Explainer Ontology is an ontology that models the technique used by an Explainer (as defined by the Explanation Ontology), to generate an Explanation. The concepts in this ontology reflect the a subset of the explanability fact sheet dimensions defined by Kacper Sokol and Peter Flach. 2020. Explainability fact sheets: a framework for systematic assessment of explainable approaches, in Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency (FAT* '20) DOI:https://doi.org/10.1145/3351095.3372870. This ontology was created as part of the iSee project (https://isee4xai.com) which received funding from EPSRC under the grant number EP/V061755/1. iSee is part of the CHIST-ERA pathfinder programme for European coordinated research on future and emerging information and communication technologies.Introduction back to ToC
Namespace declarations
| explnr | <https://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer> |
| schema | <http://schema.org> |
| explanationPattern | <http://linkedu.eu/dedalo/explanationPattern.owl> |
| void | <http://rdfs.org/ns/void> |
| owl | <http://www.w3.org/2002/07/owl> |
| resource | <http://semanticscience.org/resource> |
| xsd | <http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema> |
| protege | <http://protege.stanford.edu/plugins/owl/protege> |
| cpannotationschema | <http://www.ontologydesignpatterns.org/schemas/cpannotationschema.owl> |
| skos | <http://www.w3.org/2004/02/skos/core> |
| eo | <https://purl.org/heals/eo> |
| rdfs | <http://www.w3.org/2000/01/rdf-schema> |
| cito | <http://purl.org/spar/cito> |
| prov-o | <http://www.w3.org/TR/prov-o> |
| rdf | <http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns> |
| terms | <http://purl.org/dc/terms> |
| xml | <http://www.w3.org/XML/1998/namespace> |
| explnr | <http://www.isee4xai.com/ontologies/iseeonto/explainer> |
| vann | <http://purl.org/vocab/vann> |
| obo | <http://purl.obolibrary.org/obo> |
| prov | <http://www.w3.org/ns/prov> |
| foaf | <http://xmlns.com/foaf/0.1> |
| explainer | <http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer> |
| dc | <http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1> |
The Explainer Ontology: Overview back to ToC
This ontology has the following classes and properties.Classes
- Activation Clusters
- ALE
- Anchor
- Anchor Explanation
- Architecture Modification
- Attention Network
- Audio Modality
- Caption Generation
- Categorical
- Composite
- Computational Complexity
- Conditional Plots
- Contrasting Feature Importance Explanation
- Contrasting Gradient Technique
- Contribution Distribution Explanation
- Data Type
- Data-driven
- DeepLIFT
- DiCE
- DisCERN
- Explainability Technique
- Explainer
- Explainer Concurrentness
- Explanation Scope
- Explanation Target
- Feature Influence Explanation
- Feature Relevance
- Filter
- Game Theory Technique
- GradCam Technique
- Gradient-based Technique
- Hidden-layer Clustering
- Image
- Implementation Framework
- Individual Condition Expectation Plot
- Influence Function
- Integrated Gradient Technique
- Introspective Explanation
- Knowledge Extraction
- Layer Modification
- LIME
- Loss Modification
- Model Combination
- Neighbourhood Explanation
- Numerical
- Optimisation Based
- Ordinal
- Partial Dependence Plot
- Portability
- Probabilistic
- Prototype Explanation
- Rationalisation Explanation
- Saliency
- Saliency Map
- Semi-factual Explanation
- Sensitivity Map
- SHAP
- Simplication By Weights Dropout
- Simplification
- Simplification By Decision Tree
- Simplification By Forests
- Simplification By kNN
- Simplification By Linear Proxy Model
- Simplification By Linear Regression
- Simplification By Rule Extraction
- SmoothGrad Technique
- Statistics
- Time Complexity
- Visual Modality
- Wachter
Object Properties
- applicable problem type
- has applicable method types
- has backend
- has complexity
- has concurrentness
- has explanation scope
- has output type
- has portability
- has presentation
- is compatible with feature types
- target type
- utilises
Named Individuals
- Ante-hoc
- Any
- Categorical
- Cohort
- Constant time
- Data
- Exponential time
- Factorial time
- Global
- Image
- LightGBM
- Linearithmic time
- Local
- Log-logarithmic time
- Logarithmic time
- Model
- Model-agnostic
- Model-class specific
- Model-specific
- Multivariate
- Numerical
- Ordinal
- Post-hoc
- Prediction
- PyTorch
- Quadratic time
- Sklearn
- TensorFlow 1
- TensorFlow 2
- TensorFlow 2
- Text
- Time series
- Univariate
- XGBoost
The Explainer Ontology: Description back to ToC
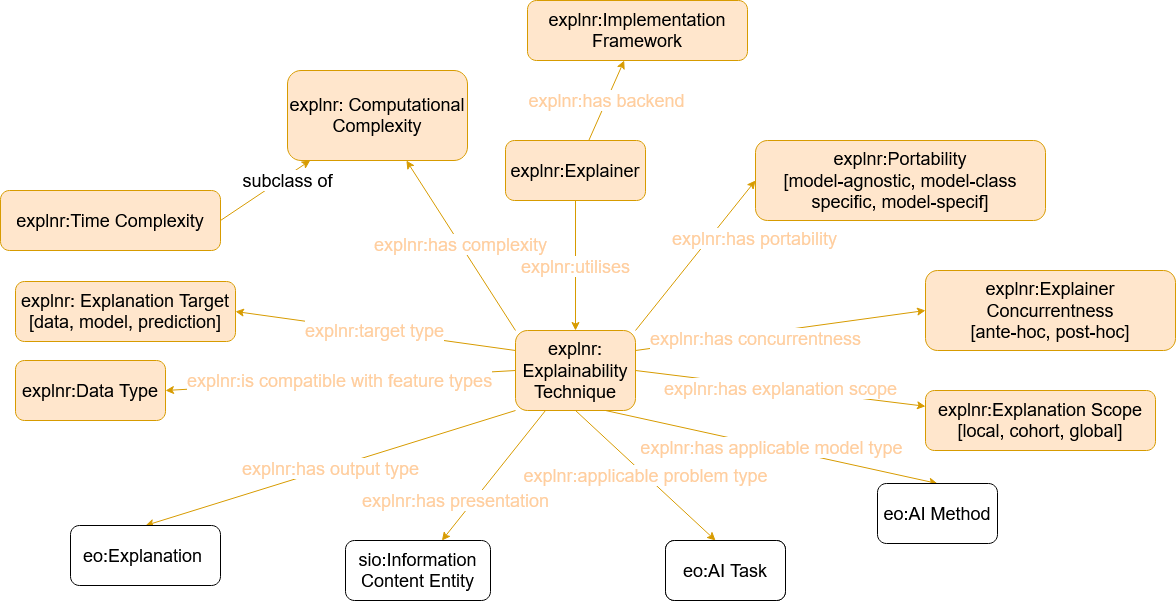
Cross reference for The Explainer Ontology classes, properties and dataproperties back to ToC
This section provides details for each class and property defined by The Explainer Ontology.Classes
- Activation Clusters
- ALE
- Anchor
- Anchor Explanation
- Architecture Modification
- Attention Network
- Audio Modality
- Caption Generation
- Categorical
- Composite
- Computational Complexity
- Conditional Plots
- Contrasting Feature Importance Explanation
- Contrasting Gradient Technique
- Contribution Distribution Explanation
- Data Type
- Data-driven
- DeepLIFT
- DiCE
- DisCERN
- Explainability Technique
- Explainer
- Explainer Concurrentness
- Explanation Scope
- Explanation Target
- Feature Influence Explanation
- Feature Relevance
- Filter
- Game Theory Technique
- GradCam Technique
- Gradient-based Technique
- Hidden-layer Clustering
- Image
- Implementation Framework
- Individual Condition Expectation Plot
- Influence Function
- Integrated Gradient Technique
- Introspective Explanation
- Knowledge Extraction
- Layer Modification
- LIME
- Loss Modification
- Model Combination
- Neighbourhood Explanation
- Numerical
- Optimisation Based
- Ordinal
- Partial Dependence Plot
- Portability
- Probabilistic
- Prototype Explanation
- Rationalisation Explanation
- Saliency
- Saliency Map
- Semi-factual Explanation
- Sensitivity Map
- SHAP
- Simplication By Weights Dropout
- Simplification
- Simplification By Decision Tree
- Simplification By Forests
- Simplification By kNN
- Simplification By Linear Proxy Model
- Simplification By Linear Regression
- Simplification By Rule Extraction
- SmoothGrad Technique
- Statistics
- Time Complexity
- Visual Modality
- Wachter
Activation Clustersc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Activation_Clusters
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
ALEc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ALE
- has super-classes
- Influence Function c
Anchorc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Anchor
- Source
- https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book/anchors.html
- has super-classes
- Simplification By Rule Extraction c
Anchor Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Anchor_Explanation
- has super-classes
- Feature Influence Explanation c
Architecture Modificationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Architecture_Modification
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
- has sub-classes
- Attention Network c, Layer Modification c, Loss Modification c, Model Combination c
Attention Networkc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Attention_Network
- has super-classes
- Architecture Modification c
Audio Modalityc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#AudioModality
- has super-classes
- explanation modality
Caption Generationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Caption_Generation
- has super-classes
- Data-driven c
Categoricalc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Categorical
- has super-classes
- Data Type c
Compositec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Composite
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
Computational Complexityc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ComputationalComplexity
- has sub-classes
- Time Complexity c
- is in range of
- has complexity op
Conditional Plotsc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Conditional_Plots
- has super-classes
- Statistics c
Contrasting Feature Importance Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Contrasting_Feature_Importance_Explanation
- has super-classes
- Feature Influence Explanation c
Contrasting Gradient Techniquec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Contrasting_Gradient_Technique
- has super-classes
- Gradient-based Technique c
Contribution Distribution Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Contribution_Distribution_Explanation
- has super-classes
- Feature Influence Explanation c
Data Typec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#DataType
- has sub-classes
- Categorical c, Image c, Numerical c, Ordinal c
- has members
- Categorical ni, Image ni, Numerical ni, Ordinal ni
Data-drivenc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Data-driven
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
- has sub-classes
- Caption Generation c, DisCERN c
DeepLIFTc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#DeepLIFT
- has super-classes
- Gradient-based Technique c
DiCEc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#DiCE
- has super-classes
- Optimisation Based c
DisCERNc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#DisCERN
- has super-classes
- Data-driven c
Explainability Techniquec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ExplainabilityTechnique
- has sub-classes
- Activation Clusters c, Architecture Modification c, Composite c, Data-driven c, Feature Relevance c, Filter c, Knowledge Extraction c, Optimisation Based c, Probabilistic c, Simplification c, Statistics c
- is in domain of
- applicable problem type op, has applicable method types op, has complexity op, has concurrentness op, has explanation scope op, has output type op, has portability op, has presentation op, target type op
- is in range of
- utilises op
Explainerc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Explainer
- has super-classes
- is in domain of
- utilises op
Explainer Concurrentnessc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ExplainerConcurrentness
- is equivalent to
- { Ante-hoc , Post-hoc }
- is in range of
- has concurrentness op
- has members
- Ante-hoc ni, Post-hoc ni
Explanation Scopec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ExplanationScope
Explanation Targetc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ExplanationTarget
- is in range of
- target type op
- has members
- Data ni, Model ni, Prediction ni
Feature Influence Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Feature_Influence_Explanation
- has super-classes
- explanation
- has sub-classes
- Anchor Explanation c, Contrasting Feature Importance Explanation c, Contribution Distribution Explanation c, Saliency Map c, Sensitivity Map c
Feature Relevancec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Feature_Relevance
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
- has sub-classes
- Game Theory Technique c, Gradient-based Technique c, Influence Function c, Saliency c
Filterc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Filter
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
Game Theory Techniquec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Game_Theory_Technique
- has super-classes
- Feature Relevance c
- has sub-classes
- SHAP c
GradCam Techniquec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#GradCam_Technique
- has super-classes
- Gradient-based Technique c
Gradient-based Techniquec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Gradient-based_Technique
- has super-classes
- Feature Relevance c
- has sub-classes
- Contrasting Gradient Technique c, DeepLIFT c, GradCam Technique c, Integrated Gradient Technique c, SmoothGrad Technique c
Hidden-layer Clusteringc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Hidden-layer_Clustering
- has super-classes
- Saliency c
Imagec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Image
- has super-classes
- Data Type c
Implementation Frameworkc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Implementation_Framework
- has members
- Any ni, LightGBM ni, PyTorch ni, Sklearn ni, TensorFlow 1 ni, TensorFlow 2 ni, XGBoost ni
Individual Condition Expectation Plotc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Individual_Condition_Expectation_Plot
- has super-classes
- Influence Function c
Influence Functionc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Influence_Function
- has super-classes
- Feature Relevance c
- has sub-classes
- ALE c, Individual Condition Expectation Plot c, Partial Dependence Plot c
Integrated Gradient Techniquec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Integrated_Gradient_Technique
- has super-classes
- Gradient-based Technique c
Introspective Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Introspective_Explanation
- has super-classes
- contextual explanation
Knowledge Extractionc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Knowledge_Extraction
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
Layer Modificationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Layer_Modification
- has super-classes
- Architecture Modification c
LIMEc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#LIME
- has super-classes
- Simplification By Linear Regression c
Loss Modificationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Loss_Modification
- has super-classes
- Architecture Modification c
Model Combinationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Model_Combination
- has super-classes
- Architecture Modification c
Neighbourhood Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Neighbourhood_Explanation
- has super-classes
- explanation
Numericalc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Numerical
- has super-classes
- Data Type c
Optimisation Basedc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Optimisation_Based
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
- has sub-classes
- DiCE c, Wachter c
Ordinalc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Ordinal
- has super-classes
- Data Type c
Partial Dependence Plotc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Partial_Dependence_Plot
- has super-classes
- Influence Function c
Portabilityc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Portability
- is in range of
- has portability op
- has members
- Model-agnostic ni, Model-class specific ni, Model-specific ni
Probabilisticc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Probabilistic
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
Prototype Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Prototype_Explanation
- has super-classes
- explanation
Rationalisation Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Rationalisation_Explanation
- has super-classes
- contextual explanation
Saliencyc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Saliency
- has super-classes
- Feature Relevance c
- has sub-classes
- Hidden-layer Clustering c
Saliency Mapc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Saliency_Map
- has super-classes
- Feature Influence Explanation c
Semi-factual Explanationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Semi-factual_Explanation
- has super-classes
- explanation
Sensitivity Mapc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Sensitivity_Map
- has super-classes
- Feature Influence Explanation c
SHAPc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SHAP
- has super-classes
- Game Theory Technique c
Simplication By Weights Dropoutc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SimplicationByWeightsDropout
- has super-classes
- Simplification c
Simplificationc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Simplification
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
- has sub-classes
- Simplication By Weights Dropout c, Simplification By Decision Tree c, Simplification By Forests c, Simplification By Linear Proxy Model c, Simplification By Linear Regression c, Simplification By Rule Extraction c, Simplification By kNN c
Simplification By Decision Treec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SimplificationByDecisionTree
- has super-classes
- Simplification c
Simplification By Forestsc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SimplificationByForests
- has super-classes
- Simplification c
Simplification By kNNc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SimplificationBykNN
- has super-classes
- Simplification c
Simplification By Linear Proxy Modelc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SimplificationByLinear_Proxy_Model
- has super-classes
- Simplification c
Simplification By Linear Regressionc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SimplificationByLinear_Regression
- has super-classes
- Simplification c
- has sub-classes
- LIME c
Simplification By Rule Extractionc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SimplificationByRule_Extraction
- has super-classes
- Simplification c
- has sub-classes
- Anchor c
SmoothGrad Techniquec back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#SmoothGrad_Technique
- has super-classes
- Gradient-based Technique c
Statisticsc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Statistics
- has super-classes
- Explainability Technique c
- has sub-classes
- Conditional Plots c
Time Complexityc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Time_Complexity
- Source
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_complexity
- has super-classes
- Computational Complexity c
- has members
- Constant time ni, Exponential time ni, Factorial time ni, Linearithmic time ni, Log-logarithmic time ni, Logarithmic time ni, Quadratic time ni
Visual Modalityc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#VisualModality
- has super-classes
- explanation modality
Wachterc back to ToC or Class ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Wachter
- Source
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.00399.pdf
- has super-classes
- Optimisation Based c
Object Properties
- applicable problem type
- has applicable method types
- has backend
- has complexity
- has concurrentness
- has explanation scope
- has output type
- has portability
- has presentation
- is compatible with feature types
- target type
- utilises
applicable problem typeop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#applicableProblemType
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- a i task
has applicable method typesop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasApplicableMethodType
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- artificial intelligence method
has backendop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasBackend
has complexityop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasComplexity
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- Computational Complexity c
has concurrentnessop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasConcurrentness
has characteristics: functional
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- Explainer Concurrentness c
has explanation scopeop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasExplanationScope
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- Explanation Scope c
has output typeop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasOutputType
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- explanation
has portabilityop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasPortability
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- Portability c
has presentationop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#hasPresentation
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- s i o 000015
is compatible with feature typesop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#isCompatibleWithFeatureTypes
target typeop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#targetType
- has domain
- Explainability Technique c
- has range
- Explanation Target c
utilisesop back to ToC or Object Property ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#utilises
- has domain
- Explainer c
- has range
- Explainability Technique c
Named Individuals
- Ante-hoc
- Any
- Categorical
- Cohort
- Constant time
- Data
- Exponential time
- Factorial time
- Global
- Image
- LightGBM
- Linearithmic time
- Local
- Log-logarithmic time
- Logarithmic time
- Model
- Model-agnostic
- Model-class specific
- Model-specific
- Multivariate
- Numerical
- Ordinal
- Post-hoc
- Prediction
- PyTorch
- Quadratic time
- Sklearn
- TensorFlow 1
- TensorFlow 2
- TensorFlow 2
- Text
- Time series
- Univariate
- XGBoost
Ante-hocni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ante-hoc
- belongs to
- Explainer Concurrentness c
Anyni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Any
- belongs to
- Implementation Framework c
Categoricalni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#categorical
- belongs to
- Data Type c
Cohortni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#cohort
- belongs to
- Explanation Scope c
Constant timeni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Constant_time
- belongs to
- Time Complexity c
Datani back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#data
- belongs to
- Explanation Target c
Exponential timeni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Exponential_time
- belongs to
- Time Complexity c
Factorial timeni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Factorial_time
- belongs to
- Time Complexity c
Globalni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#global
- belongs to
- Explanation Scope c
Imageni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#image
- belongs to
- Data Type c
- dataset type c
LightGBMni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#LightGBM
- belongs to
- Implementation Framework c
Linearithmic timeni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Linearithmic_time
- belongs to
- Time Complexity c
Localni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#local
- belongs to
- Explanation Scope c
Log-logarithmic timeni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Log-logarithmic_time
- belongs to
- Time Complexity c
Logarithmic timeni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Logarithmic_time
- belongs to
- Time Complexity c
Modelni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#model
- belongs to
- Explanation Target c
Model-agnosticni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#model-agnostic
- belongs to
- Portability c
Model-class specificni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#modelClassSpecific
- belongs to
- Portability c
Model-specificni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#modelSpecific
- belongs to
- Portability c
Multivariateni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#multivariate
- belongs to
- dataset type c
Numericalni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#numerical
- belongs to
- Data Type c
Ordinalni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#ordinal
- belongs to
- Data Type c
Post-hocni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#post-hoc
- belongs to
- Explainer Concurrentness c
Predictionni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#prediction
- belongs to
- Explanation Target c
PyTorchni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#PyTorch
- belongs to
- Implementation Framework c
Quadratic timeni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Quadratic_time
- belongs to
- Time Complexity c
Sklearnni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#Sklearn
- belongs to
- Implementation Framework c
TensorFlow 1ni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#TensorFlow1
- belongs to
- Implementation Framework c
TensorFlow 2ni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#TensorFlow2
- belongs to
- Implementation Framework c
TensorFlow 2ni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#TensowFlow2
Textni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#text
- belongs to
- dataset type c
Time seriesni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#time_series
- belongs to
- dataset type c
Univariateni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#univariate
- belongs to
- dataset type c
XGBoostni back to ToC or Named Individual ToC
IRI: http://www.w3id.org/iSeeOnto/explainer#XGBoost
- belongs to
- Implementation Framework c
Legend back to ToC
op: Object Properties
dp: Data Properties
ni: Named Individuals
References back to ToC
Add your references here. It is recommended to have them as a list.Acknowledgments back to ToC
The authors would like to thank Silvio Peroni for developing LODE, a Live OWL Documentation Environment, which is used for representing the Cross Referencing Section of this document and Daniel Garijo for developing Widoco, the program used to create the template used in this documentation.

